
As per the reports, Google's AI firm DeepMind will be using AI practices and tools to study changes in the human DNA that can cause diseases. The target of the study is to ensure that any mutations occurring in the human DNA are pinpointed before they can cause adverse consequences.
So far, collaboration between DeepMind and researchers has helped pinpoint more than 85% of key mutations that will help in mitigating any instances occurring from them. In addition, the collaboration is meant to speed diagnosis as well as research so that treatments for mutations can be identified without any hassle.
Another benefit of using AI in terms of studying DNA changes is that it'll allow us to pinpoint areas that need focus, helping to find the cause and the cure. Previously, it took quite a time for the researchers to identify changes to the DNA as well as come up with a cure for the mutation.
However, with this big step, the researchers will be able to cut short the timeline, and be proactive in terms of identification, mitigation, and cure. The new system will seamlessly allow researchers to share and obtain data via the internet, helping them proceed to the next stages of the research.
How Will The Technique Work?
It's not as simple as said. Identifying mutations in the DNA takes immense precision so that results can be formulated accordingly. However, using AI, the researchers will identify the order of the components in the DNA strands.
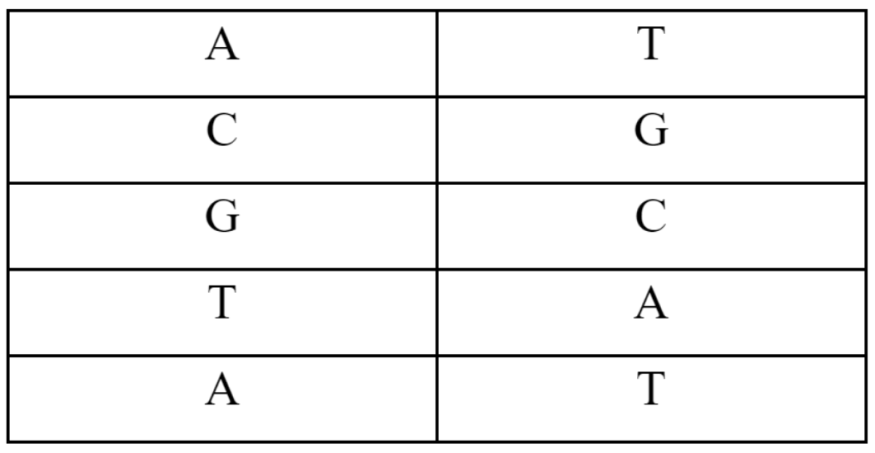
The DNA is made of four blocks, comprising Adenine (A), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G), and Thymine (T). When an embryo is developing, the order of these letters is read to produce proteins. These proteins act as a building block for cells and tissues, which ultimately make the parts of the body.
In case of a mutation, the letters are read wrong, resulting in incomplete or disoriented creation of body cells and tissues, causing a disease. Hence, it's important that the order of the DNA blocks is read properly, which is why it's important that any mutation in this process is identified.
The AlphaMissense
DeepMind's AI worked out nearly all shapes of the protein in the human body. Using the instances and research, a new system called the AlphaMissense has been developed. This system will be the key to identifying mutations in the DNA strand.
The system will study human body proteins, checking if the letters will produce the correct protein shape or not. In case it doesn't, the system will identify it as a disease-causing protein and will notify the researchers.
Here's a visual display of how the system works:
All organisms are built from DNA. A, C, G, and T represent the building blocks of the DNA. AlphaMissense identifies the changes in the DNA strand, terming it a mutation:
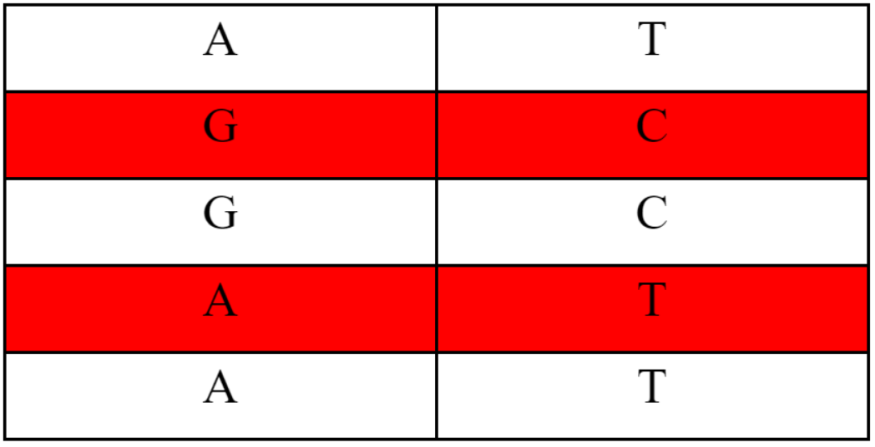
The Need of the Hour and Future Applications
The need for such contributions is immense since the researchers have no to little knowledge of what areas of the human DNA can be affected and lead to a disease. As per the current reports, only 0.1% of letter changes or said mutations have been reported so far, deemed benign/disease-causing.
However, Pushmeet Kohli, VP of DeepMind, stated that with the current system, these figures have gone up to 89%. Instead of researching chemical building blocks while waiting for data from other researchers, the researchers can now focus on new areas, and work more swiftly.
In addition, Genomics England has also tested the latest tool, and as per Dr. Ellen Thomas, Deputy Chief Medical Officer at Genomics, England, the organization will be the first to benefit from the new system's implementation.
The tool/ system holds great importance as it brings a new perspective to the data, helping scientists and researchers comprehend genetics easily and more practically. Using this, patients can be dealt with in effective clinical terms.
Moreover, the system can also become a great contributor to molecular biology as well as aid in life science studies.
© 2026 NatureWorldNews.com All rights reserved. Do not reproduce without permission.





