Sunspots are known for their presence on the Sun's surface as circular or planet-size regions. Their size varies depending on the region, with some smaller or larger than the others.
In the latest space developments, a giant sunspot facing Earth has been detected.
The sunspot is known as AR3038 and is reportedly being monitored by the Solar Dynamics Observatory of National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA).
AR3038 has doubled its size in the past 24 hours as of Monday evening, June 20.
Colossal Sunspot
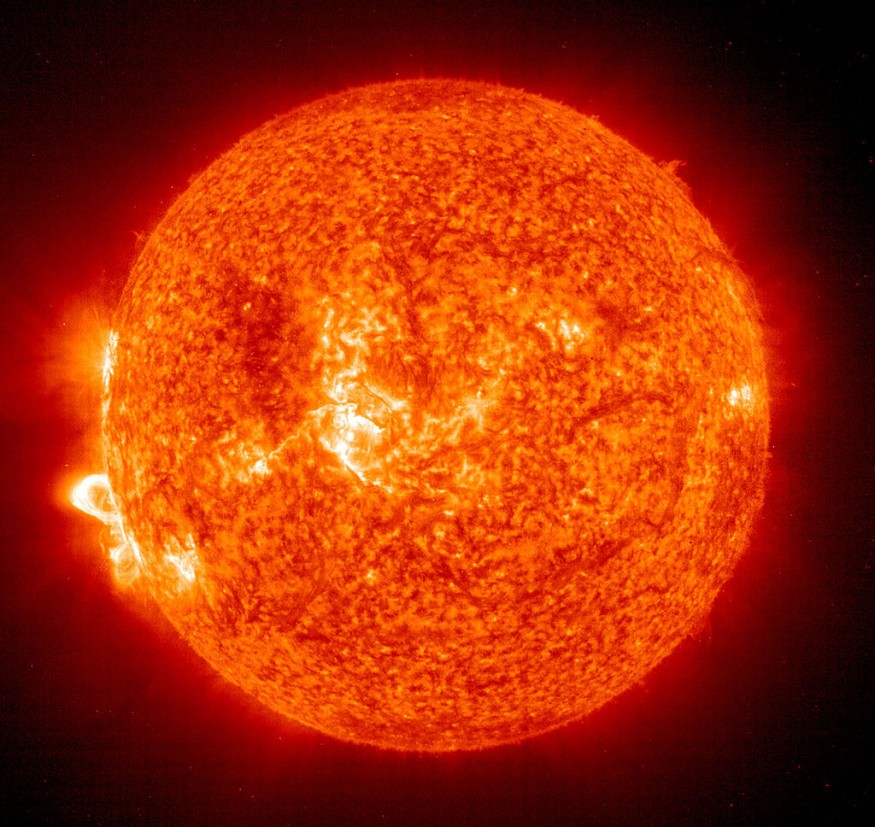
The growing sunspot is yet to hit Earth but reports suggested that there is a chance for it to occur. This is due to the trajectory between AR3038 and Earth, as cited by msn.com.
The size of the solar spot is only the tip of the iceberg as its potential to release a solar flare at any time is what matters.
What is a Sunspot?
Sunspots are regions of the Sun which are relatively darker and cooler than other areas on the Sun's surface, according to the NASA.
These so-called "dark spots" have been considered as a gateway for solar storms, such as solar flares.
The US space agency added that sunspots can reach temperatures by up to 6,500 degrees Fahrenheit.
While this temperature is extremely hot , it is nothing compared to other parts of the Sun that can reach nearly 10,000 degrees Fahrenheit.
NASA explained that sunspots are relatively cool since they form in areas where magnetic field in our solar system's only star are stronger than normal.
The intensity of the magnetic force is enough to prevent heat within the Sun from reaching the surface.
In the past, sunspots have released solar flares; wherein some face toward the Earth while some do not.
On April 30, an active yet departing sunspot called AR2994, or Active Region 2994, released an X-class solar flare.
The said class is the most powerful explosion in the Sun, according to space.com.
Solar Flare
The Sun is a hot ball of gas and its underlying layers consist magnetic field lines, which often come across with one another similar to the entanglement of strings.
NASA underlined that an abrupt explosion of energy transpires called a solar flare.
Solar flares are only one of the two main types of solar storms, with the other being coronal mass ejections (CMEs).
While different in the manner of explosion, both space storms release an intense solar radiation or high-energy particles into space.
Space Weather Events
These particles may take the form of one or some of the following space weather event types laid out by the Space Weather Prediction Center (SWPC):
- Geomagnetic storms
- Solar radiation storms
- Radio blackouts
In general, these events cause disruption to Earth's magnetosphere, a layer in our planet's atmosphere, which is responsible for protecting us from solar storms, solar radiation, and cosmic particle radiation, as well as solar winds.
A direct strike of magnetic storms and radio blackouts to the magnetosphere disrupts satellite and radio technology, mainly affecting signal and communication.
Meanwhile, solar radiation storms affect mainly biological organisms, including animals and humans.
Sunburn is one of the many effects of a solar radiation damage to humans.
© 2026 NatureWorldNews.com All rights reserved. Do not reproduce without permission.





