Scientists found an abundant marine ecosystem and communities on the South of Wellington and Kapiti coast.
Some marine animals are undescribed and unknown.
Researchers have been on the quest to discover the secrets of oceans. Special equipment is essential to unearth unknown species to science.
Learning new species can help experts track their populations and save them from threats, including habitat loss and shipping collision.
According to NOAA Ocean Exploration, scientists managed to explore a small part of the oceans, noting that deep sea waters are largely unknown to science.
As of this year, NOAA showed that about 24.9% global sea floor was already mapped by experts using advanced technology.
On the South of Wellington's and Kapiti coast, the areas are considered rich in biodiversity and coral reef systems.
Wellington South Coast and Marine Life
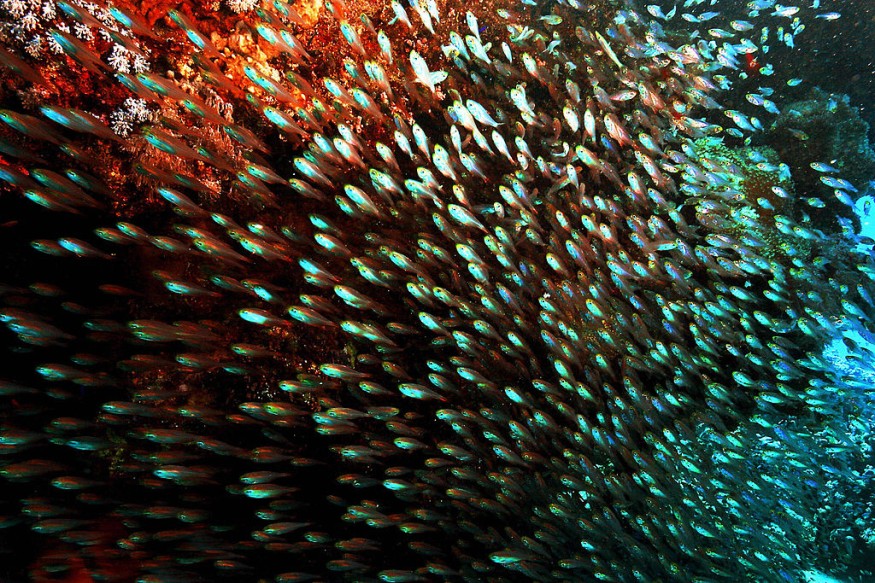
In a recent report, the Department of Conservation explained that the Wellington coast has important marine communities.
In 2019, researchers discovered an unusual fish, half-naked hatchetfish, and hula skirt siphonophore.
As a result, experts from the Te Herenga Waka-Victoria University of Wellington looked into the coast and found something new and stunning biodiversity on the coast.
According to marine biologist and Professor James Bell, the marine environment on Wellington's coast has unknown marine areas.
The researchers underwent an exploration of the area's deep waters. Researchers explored at least 18 sites, with a depth of 26 to 72 meters.
Professor Bell added that the marine communities have stunning coral reefs and branching sponges. They also found rich sponges and bryozoans (moss animals).
The report added that the 18 sites are not considered protected.
The Missouri Department of Conservation explained that bryozoans are small aquatic animals that thrive in colonies.
Bryozoans are essential for the marine environment. They also live in freshwater, swamps, ponds and lakes.
In addition, Professor Bell explained that the discovered marine communities and animals were amazing, which is different from shallow waters.
In the Kāpiti Coast marine communities, the researchers also found octopus, hagfish, sharks and blue cod.
However, the report raised concerns that the 18 sites they explored were unprotected. The species under the deep waters and coral reef systems could likely suffer from habitat loss and overfishing threats.
Also Read : Climate Change Threatens Sea Urchin Survival That Can Devastatingly Affect Coral Reef Growth
Marine conservation of coral reef systems and aquatic species
NOAA explained that coral reefs are essential for biodiversity and marine animals.
According to the report, at least 25% of fish are dependent on coral reef systems. The decline of the reef system can affect fish and other aquatic species.
As a result, mapping the ocean floor and deep water discovery is essential to protect and conserve marine environments, known and unknown to science.
Recently, a study published in the Journal of Experimental Biology showed the impact of extreme weather events on sea urchin populations.
Sea urchins are vital for ecosystems as natural engineers.
Excessive rainfall could likely result in different salinity water levels, which sea urchins are sensitive.
Related Article : Florida Ocean Temperature Reaches Over 100 Degrees; Temp Likely to Become World Record
For more similar stories, don't forget to follow Nature World News.
© 2026 NatureWorldNews.com All rights reserved. Do not reproduce without permission.





