Recent reports showed that climate change and ocean acidification could affect marine animals and organisms, including the Red Sea Urchin in Southern California.
Scientists and researchers have raised concerns over the impact of climate change and the warming of waters on marine biodiversity.
Aquatic animals are sensitive to water temperatures, and it would become difficult for them to adapt, especially coral reef system.
According to recent research, sea urchins in Northern and Southern California adapted to their environment despite rising global temperatures.
Red sea urchins
The research findings were published in Science Advances, and it is also available to read on the Phys.org website.
Unlike other marine animals, the study explained that the sea urchins' population adapted to the challenging warmer conditions.
However, the researchers emphasized that the worsening warming of their environment would turn difficult for them to tolerate.
According to the report, the study's first author Emily Donham, from UC Santa Barbara, explained that red sea urchins are a significant part of the coast.
In fact, the urgency of understanding the effect of climate change on their species is essential.
The Sea Grant California said red sea urchins (strongylocentrotus franciscanus) have unique arms for food and cleaning.
The report noted that the species is considered sensitive to water temperatures.
Meanwhile, the study's senior author Prof. Kristy Kroeker explained that the Southern California red sea urchins were more sensitive to environmental changes than the urchins in Northern California.
Professor Kroker is also from UC Santa Cruz.
The study investigated how the red sea urchins coped with changing temperatures in terms of water temperatures, ocean acidification and dissolved oxygen.
Furthermore, the researchers looked into the differences of red sea urchins in Northern and Southern California.
For the red sea urchins found in the Southern parts, the study noted that the species experienced an acidic and colder environment.
The research added that the Southern California sea urchins would become the most affected by environmental conditions and warming of the environment.
Although the red sea urchins have adapted to their local environmental conditions, some populations in other parts of the globe could find it challenging to thrive.
Nature of Red Sea Urchin
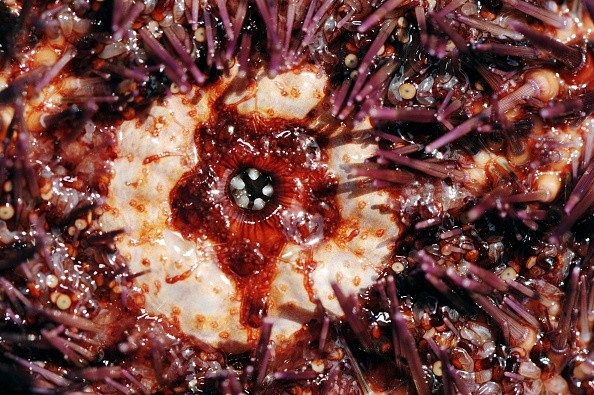
According to the Sea Grant California, red sea urchin is considered echinoderm that can also thrive in Baja California, Alaska and North American coasts.
The report added that the red sea urchins would emerge from June to November in San Diego.
Also Read : Rain, Snow To Unload in Portions of Northeast This Week; Snowfall To Unfold in New York, Michigan
On the other hand, Marine Species Wildlife California explained that the red sea urchin could live in coastal waters or areas with abundant kelp.
- They also have a long lifespan: 50 years in California and about 100 years on West Coast.
- They can also live up to 200 years.
Furthermore, the Central Coast Biodiversity said that red sea urchin is also known as a ball of spines with noticeable red color.
Did you know?
Alaska's Department of Fish says the red sea urchin can have red and dark colors. They are also known as the largest sea urchin species.
They might look like without feet, but they have!
For more similar, don't forget to follow Nature World News.
© 2026 NatureWorldNews.com All rights reserved. Do not reproduce without permission.





